Forskel mellem versioner af "Limbiske system"
| Linje 1: | Linje 1: | ||
[[Fil:Limbic1.png|400px|thumb|right|Fig. 1 Det limbiske system]] | [[Fil:Limbic1.png|400px|thumb|right|Fig. 1 Det limbiske system]] | ||
== Introduktion == | == Introduktion == | ||
| − | Det limbiske system, | + | Det limbiske system er den udviklingsmæssige ældste del af hjernen, som i modsætning til neocortex der typisk består af 6 cellelag, har færre cellelag, nedtil 1 cellelag i hippocampus. |
| − | Det limbiske | + | Det limbiske lap opfattes nogle gange som en hjernelap, ligesom eksempelvis frontallappen eller temporallappen. Den limbiske lap udgør ikke hele det limbiske system med udgøres af gyrus cinguli og tilstødende cortical strukturer: |
| + | * Det subcallosale område anteriort | ||
| + | * Gyrus cingulus | ||
| + | * Isthmus | ||
| + | * Gyrus parahippocampale inferiort | ||
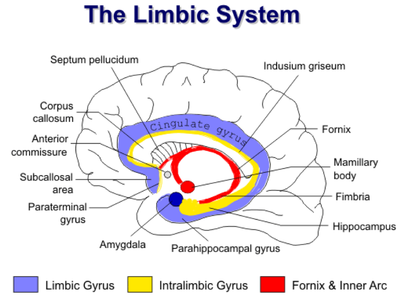
Som det fremgår af figur 1 udgør det limbisk system flere koncentriske C-formede strukturer som strækker sig rundt om copus callosum fra gyrus cingulis subcallosale område anteriort under rostrum af corpus callosum, posteriort forbi, parietallappen, occipitallappen og ned i temporallappen. | Som det fremgår af figur 1 udgør det limbisk system flere koncentriske C-formede strukturer som strækker sig rundt om copus callosum fra gyrus cingulis subcallosale område anteriort under rostrum af corpus callosum, posteriort forbi, parietallappen, occipitallappen og ned i temporallappen. | ||
| Linje 20: | Linje 24: | ||
Nogle gange regnes den orbitofrontal cortex med til det limbiske system | Nogle gange regnes den orbitofrontal cortex med til det limbiske system | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Funktion == | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | The limbic system operates by influencing the endocrine system and the autonomic nervous system. It is highly interconnected with the nucleus accumbens, the brain's pleasure center, which plays a role in sexual arousal and the "high" derived from certain recreational drugs. These responses are heavily modulated by dopaminergic projections from the limbic system. In 1954, Olds and Milner found that rats with metal electrodes implanted into their nucleus accumbens as well as their septal nuclei repeatedly pressed a lever activating this region, and did so in preference to eating and drinking, eventually dying of exhaustion.[6] | ||
| + | The limbic system is also tightly connected to the prefrontal cortex. Some scientists contend that this connection is related to the pleasure obtained from solving problems. To cure severe emotional disorders, this connection was sometimes surgically severed, a procedure of psychosurgery, called a prefrontal lobotomy (this is actually a misnomer). Patients who underwent this procedure often became passive and lacked all motivation. | ||
Versionen fra 7. okt 2012, 10:41
Introduktion
Det limbiske system er den udviklingsmæssige ældste del af hjernen, som i modsætning til neocortex der typisk består af 6 cellelag, har færre cellelag, nedtil 1 cellelag i hippocampus.
Det limbiske lap opfattes nogle gange som en hjernelap, ligesom eksempelvis frontallappen eller temporallappen. Den limbiske lap udgør ikke hele det limbiske system med udgøres af gyrus cinguli og tilstødende cortical strukturer:
- Det subcallosale område anteriort
- Gyrus cingulus
- Isthmus
- Gyrus parahippocampale inferiort
Som det fremgår af figur 1 udgør det limbisk system flere koncentriske C-formede strukturer som strækker sig rundt om copus callosum fra gyrus cingulis subcallosale område anteriort under rostrum af corpus callosum, posteriort forbi, parietallappen, occipitallappen og ned i temporallappen.
Bestandele af det limbiske system
- Hippocampus
- Amygdala
- Fornix
- Copora Mammilare
- Nucleus Septalis
- Gyrus parahippocampale
- Gyrus Cingulus
- Gyrus Dentatus
- Entorhinal cortex (del af gyrus parahippocampale)
- Nucleus Accumbens
Nogle gange regnes den orbitofrontal cortex med til det limbiske system
Funktion
The limbic system operates by influencing the endocrine system and the autonomic nervous system. It is highly interconnected with the nucleus accumbens, the brain's pleasure center, which plays a role in sexual arousal and the "high" derived from certain recreational drugs. These responses are heavily modulated by dopaminergic projections from the limbic system. In 1954, Olds and Milner found that rats with metal electrodes implanted into their nucleus accumbens as well as their septal nuclei repeatedly pressed a lever activating this region, and did so in preference to eating and drinking, eventually dying of exhaustion.[6] The limbic system is also tightly connected to the prefrontal cortex. Some scientists contend that this connection is related to the pleasure obtained from solving problems. To cure severe emotional disorders, this connection was sometimes surgically severed, a procedure of psychosurgery, called a prefrontal lobotomy (this is actually a misnomer). Patients who underwent this procedure often became passive and lacked all motivation.